Nuts are known to be a relatively healthy option to snack on because of their heart health benefits, healthy fat content, protein, and fibre. On the other hand, some find that consuming nuts results in some discomfort in the tummy or gastrointestinal issues.
According to research, the leading causes of stomach pain, especially after eating nuts, include nut allergies or intolerances, high-fat content, fibre, and the presence of antinutrients such as phytic acid and tannins.
However, it is possible to suggest some reasonable advice on how to decrease or avoid stomach pain after nut consumption: limiting portions, soaking/raw or roasting nuts, or slowly increasing fibre intake.
Not only does this make nuts a good source of food to incorporate into a healthy diet, but it is also essential to know the possible causes of stomach pain after consuming them.
This article will explore 4 reasons for stomach pain after eating nuts and what to do about it.
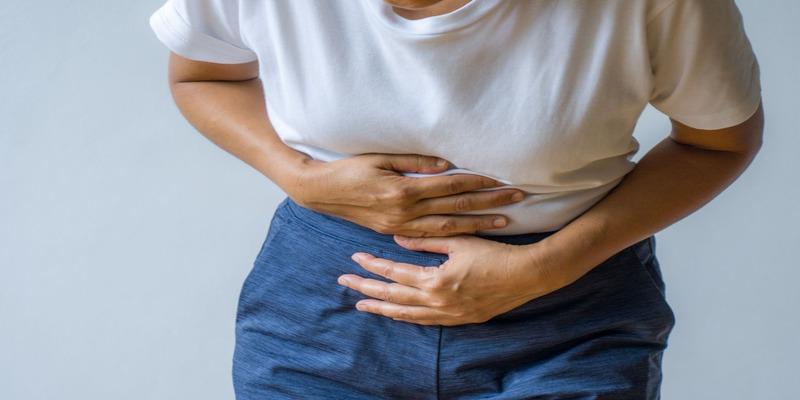

Food allergy is one of the severe causes of stomach pains after consuming nuts. Tree nut allergies, which include almonds, walnuts, cashews, and pistachio allergies, may lead to various allergic symptoms that would impact the digestive system.
Some initial manifestations of an allergy might include stomach discomfort and, consequently, pain, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea.
It should also be noted that nut intolerance is different from allergies, and it usually does not affect the immune system. While it may not cause the usual symptoms associated with it, such as bloating and stomach pain, gas, and diarrhea, it is still capable of causing these symptoms in your digestive system.
Intolerance symptoms are less likely to occur as quickly as allergic reactions, playing out several hours after consuming the substance.
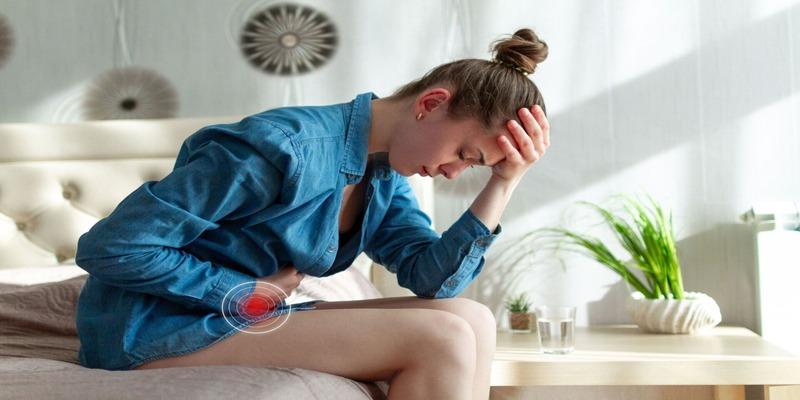

Nuts, as expected, are rich sources of fat, which are, however, healthy for the system; this may be a source of worry for those with sensitive stomachs.
The fat in nuts is challenging to break down, and some people may encounter problems if they are suffering from IBS or gallbladder problems or if they experience any trouble consuming fattening foods.
Excessive intake of fats leads to the slowing down of the stomach emptying system, resulting in bloating, stomach discomfort, and pain.
For instance, when you take foods with a high-fat content, such as nuts, the body has to secrete more bile to digest the fat.
If you have a bile-related issue, such as gallbladder dysfunction, or your digestive system is sensitive to high-fat foods, this process may lead to cramping and pain.
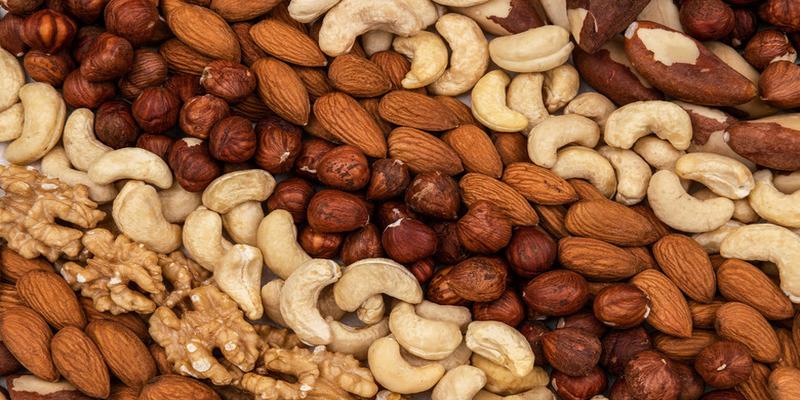

According to nutritional content, nuts are packed with dietary fiber, which is suitable for the digestive system as long as they are taken in moderation.
Nonetheless, moderation when consuming nuts can be detrimental since consuming too many of them will make the intake of fiber high, and this causes several digestive problems such as bloating, gas, constipation, or diarrhea.
Fiber aids in maintaining bowel movement because it increases the volume of the stool and promotes movement in the gut. But if the fiber intake is done excessively, the fiber ferments in the stomach, thus leading to the formation of gases in the tummy and, thus, bloating.
Fiber from the skins of nuts can be especially problematic to digestive systems due to their insolubility, and this may be worse for people with sensitive tummies or those with existing health complications in the digestive tract, such as IBS.
Most nuts have compounds known as antinutrients, including phytic acid and tannins, that hinder digestion and cause stomach upsets. Phytic acid chelates with minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and iron, and hence, its uptake from the gut is limited.
Tannins are a kind of polyphenol that can cause irritation to the mucous membrane in the stomach and lead to such adverse effects as bloating, gas, and stomach pain.
Phytic acid and tannins are present in the outer layers of nuts and seeds as a natural defense mechanism. While they have some health benefits, such as acting as antioxidants, they can also cause digestive issues in people with sensitive stomachs or those who consume large quantities of raw nuts.
This acid can contribute to mineral deficiencies over time, while tannins may cause nausea or indigestion in some individuals.
It is recommended to take nuts occasionally and not take large quantities of raw nuts at a particular time since this may cause digestive problems.
All in all, if you analyze the causes that make you uncomfortable with nuts, you can prevent these problems and continue to receive all the valuable nutrients included in nuts. If the symptoms continue, it is advisable to seek a doctors opinion to ensure that it is just a viral infection and not something else.
You may take it seriously if you have experienced these 4 reasons for stomach pain after eating nuts and what to do about it. Otherwise, it may be harmful to you.

By Darnell Malan/Sep 25, 2024
By Madison Evans/Sep 21, 2024

By Susan Kelly/Aug 24, 2024

By Georgia Vincent/Sep 25, 2024

By Aldrich Acheson/Oct 24, 2024

By Maurice Oliver/Sep 20, 2024

By Aldrich Acheson/Sep 06, 2024

By Elena Davis/Sep 26, 2024

By Pamela Andrew/Sep 25, 2024

By Pamela Andrew/Oct 25, 2024

By Gabrielle Bennett/Sep 26, 2024

By Kristina Cappetta/Sep 20, 2024